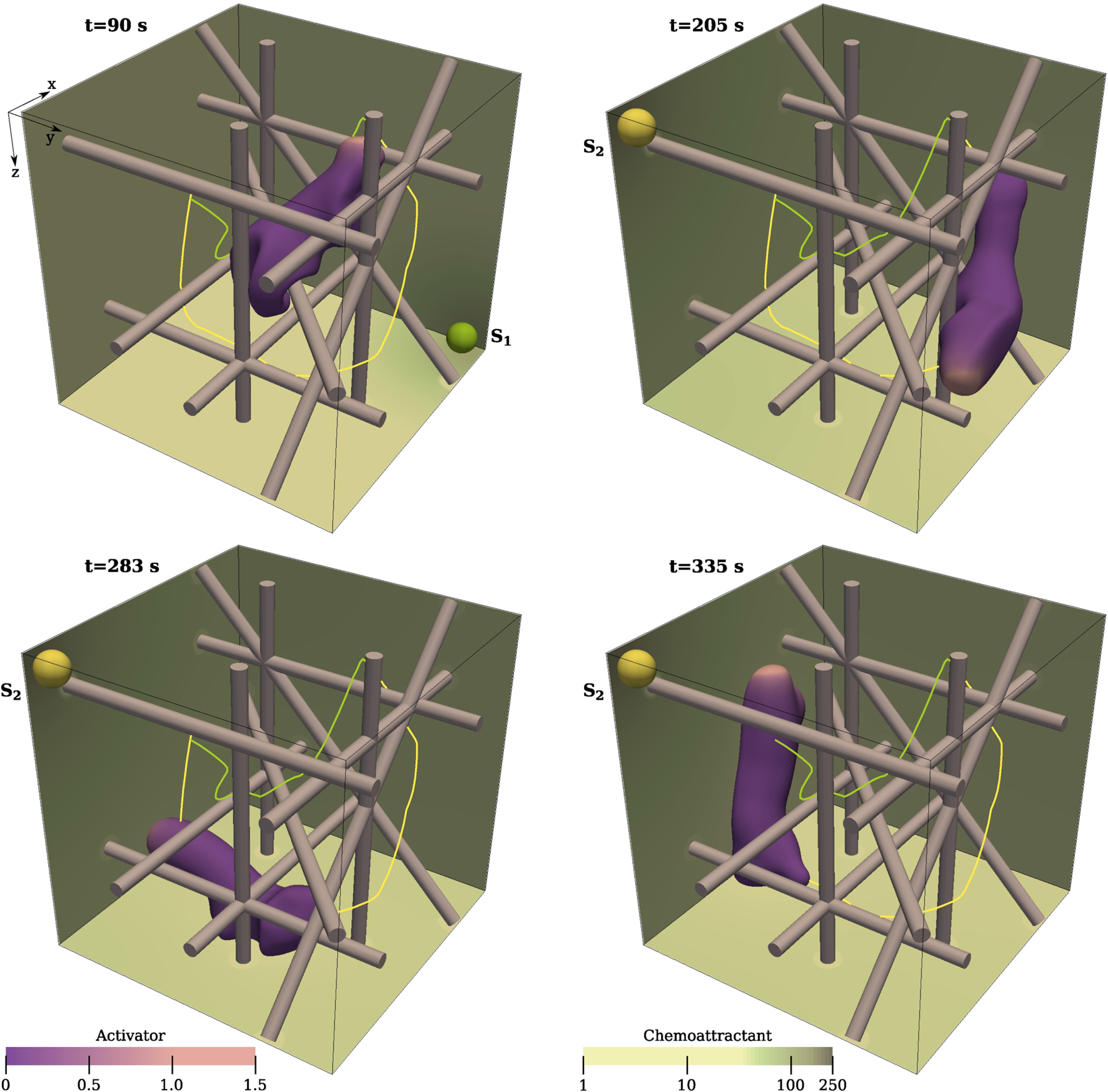
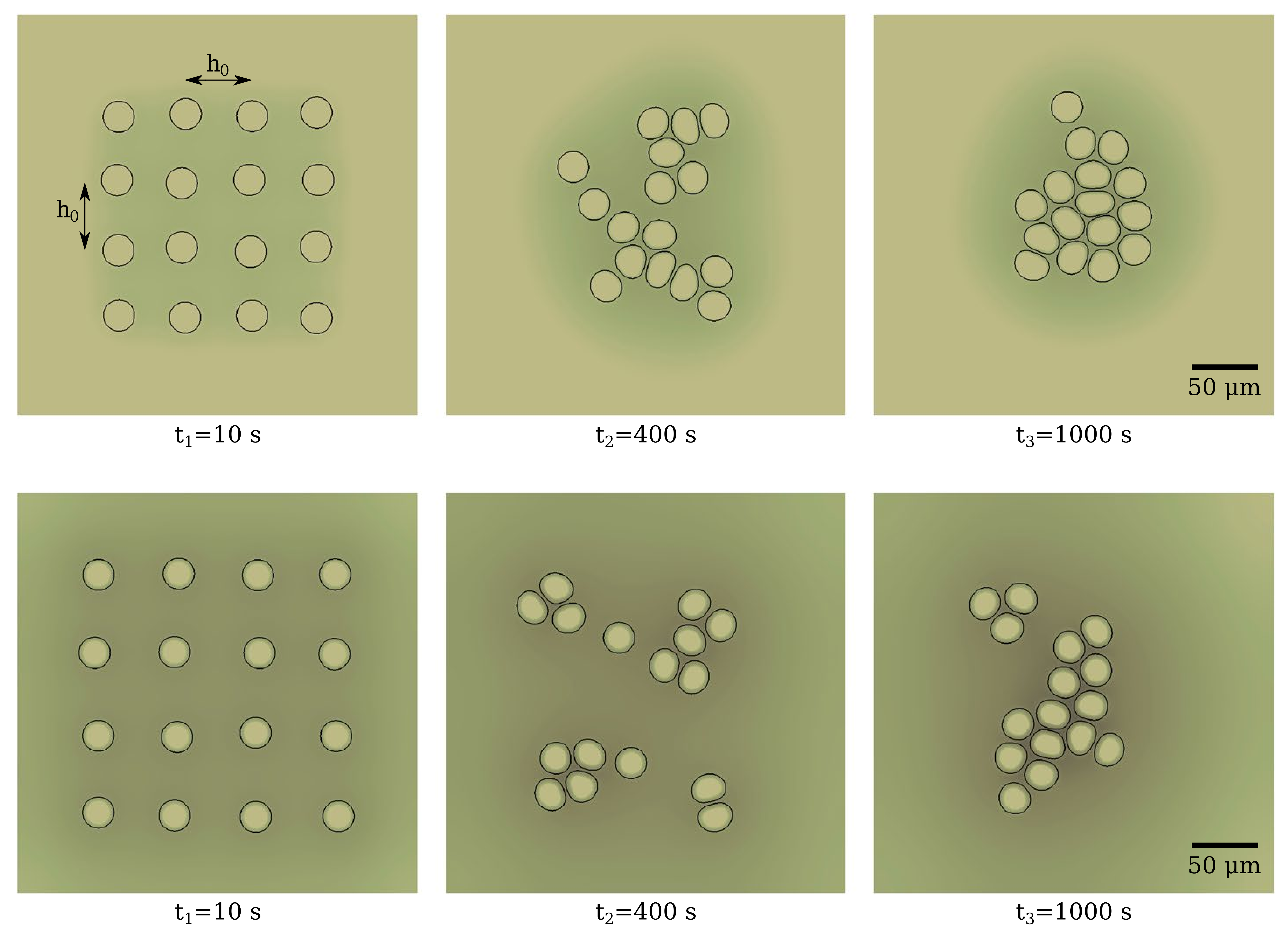
Both individual and collective cell migration regulate key biological functions such as tissue formation, wound healing, or cancer metastasis. Cell motion results from complex intra- and extra-cellular mechanochemical interactions. The phase-field method allows me to track the cell shape, localize the dynamics of different compounds to moving volumes (cell's interior and exterior) and surfaces (cell's membrane), and control multicellular systems through an energy functional. The pictures show individual cell chemotaxis in a fibrous environment (left) and cell co-attraction in non-confluent multicellular systems (right).
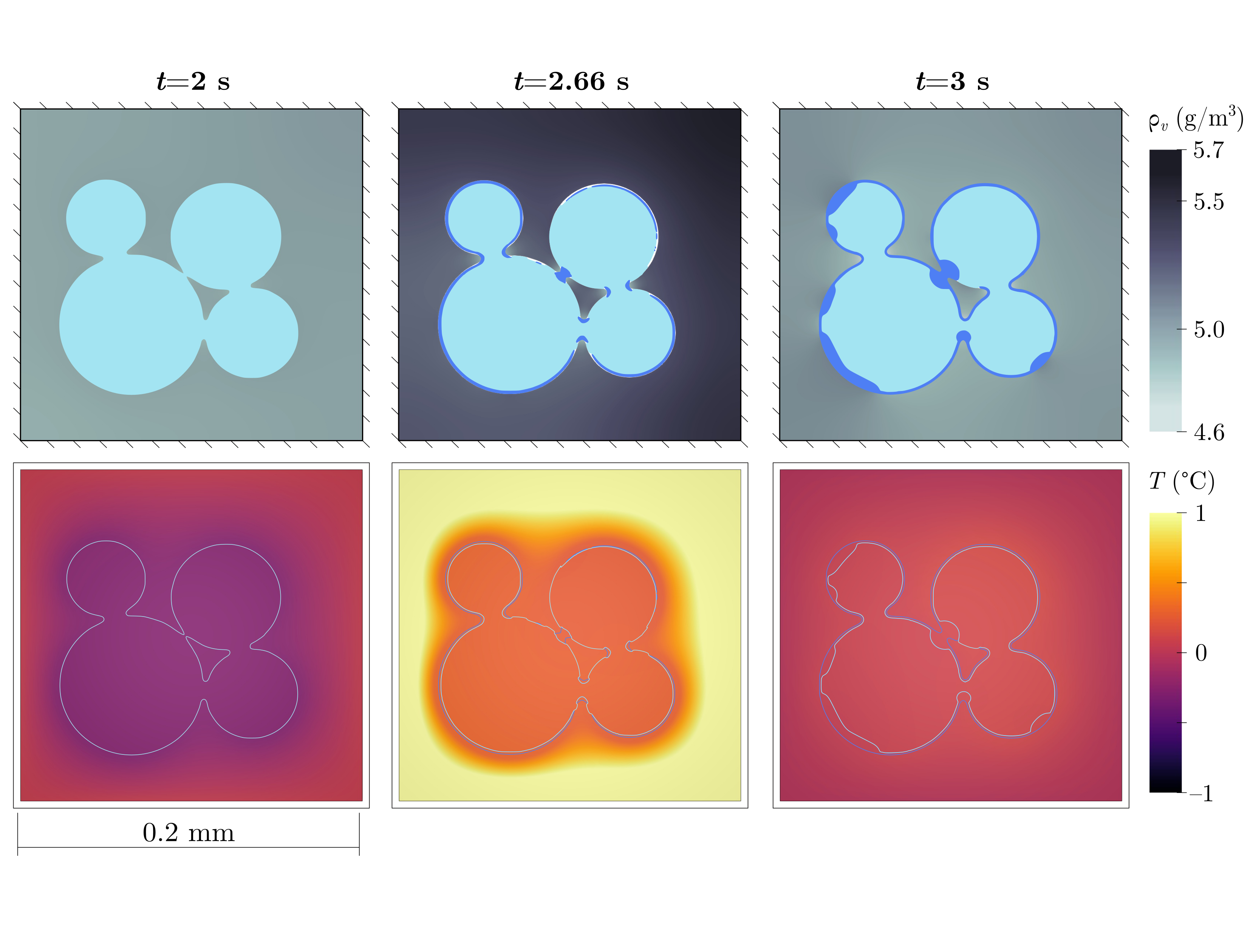
Snow is a heterogeneous porous material composed of ice, liquid water, and air. Complex processes such as preferential meltwater infiltration or ice piping affect the hydraulic, thermal, and mechanical properties of the snow. I model the phase transitions of the different phases (ice, liquid water, and air) at the microscopic scale to reproduce snow metamorphism. I also derived a model for meltwater infiltration at the macroscopic scale (~meter), which enables better prediction of meltwater infiltration and improved management of water resources. The picture displays water vapor concentration, ice, liquid water, and temperature during a snow melting event.
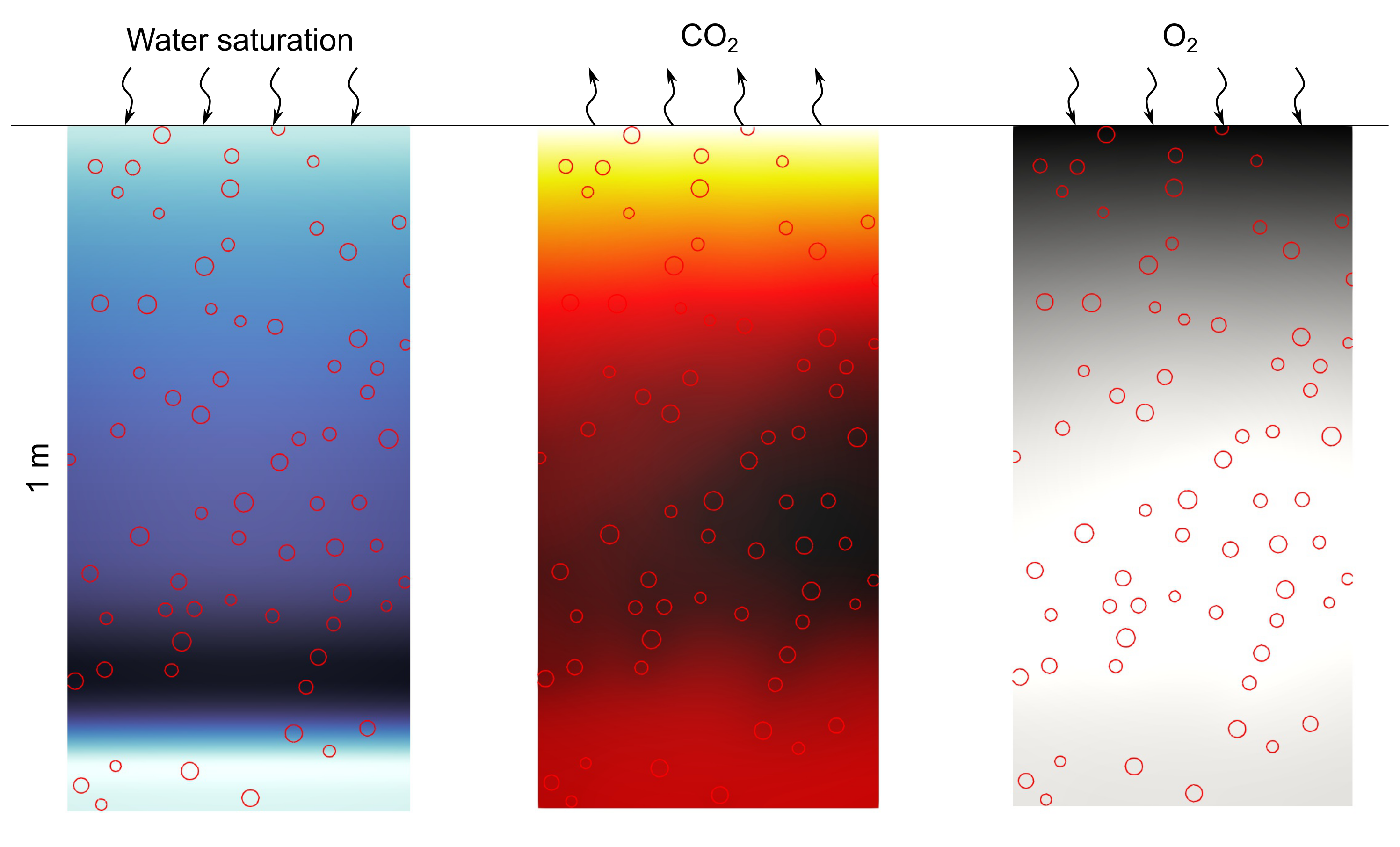
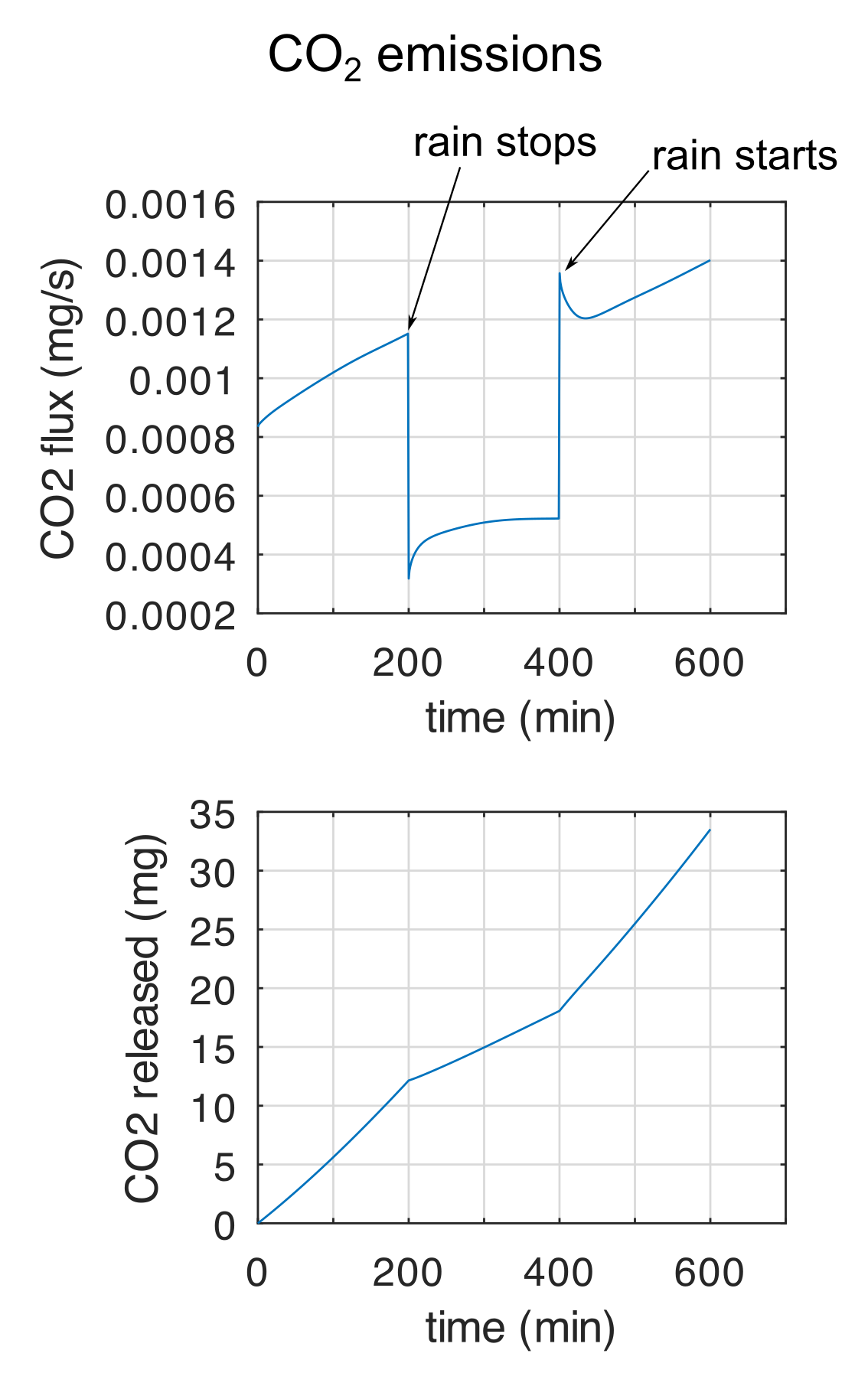
Soil organic matter represents the second largest reservoir of carbon in Earth. Microbial respiration, which is mediated by soil moisture, temperature, and soil structure, dictates CH4 and CO2 fluxes into the atmosphere. I develop a Darcy-scale model that couples biogeochemical processes under a reactive-transport framework to capture soil decomposition and gas generation. The model accounts for water infiltration and soil and organic matter heterogeneity. The figure in the left shows the water saturation, CO2 and O2 concentrations caused by aerobic respiration during a drainage event. Red circles represent organic matter aggregates. In the right, CO2 flux and accumulated CO2 released to the atmosphere.
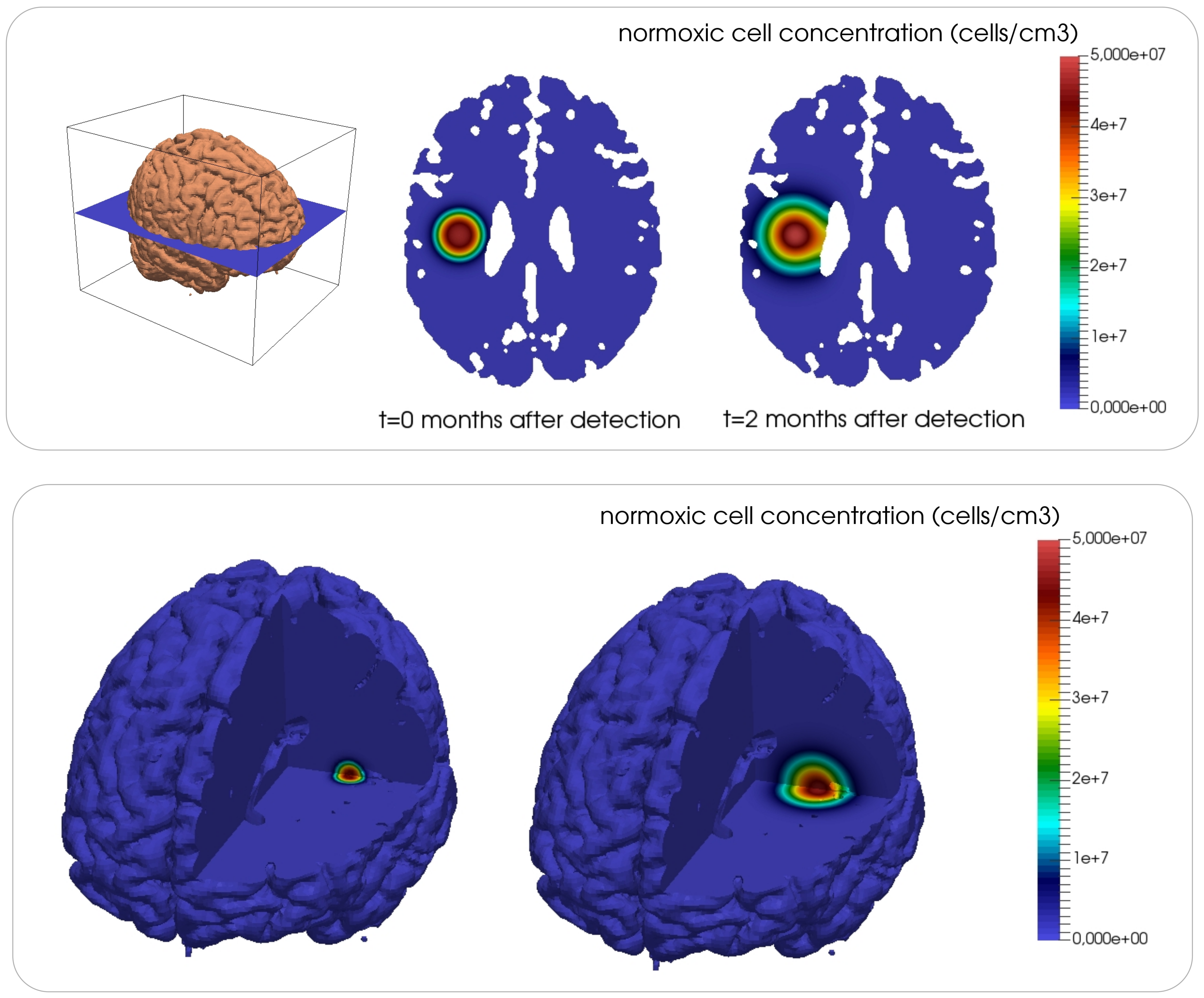
I have studied angiogenesis and glioma growth. Angiogenesis is the growth of new capillaries induced by tumors. The new capillaries provide an extra supply of oxygen to the tumor, which is essential to continue the tumor growth. Capillaries are localized through the phase-field method. Glioma is a highly malignant tumor that forms in the glial cells of the brain. I used the phase-field method to localize the dynamics of tumor cells, vasculature, and angiogenic factors to the brain geometry. The picture shows the time evolution of the concentration of normoxic tumor cells.
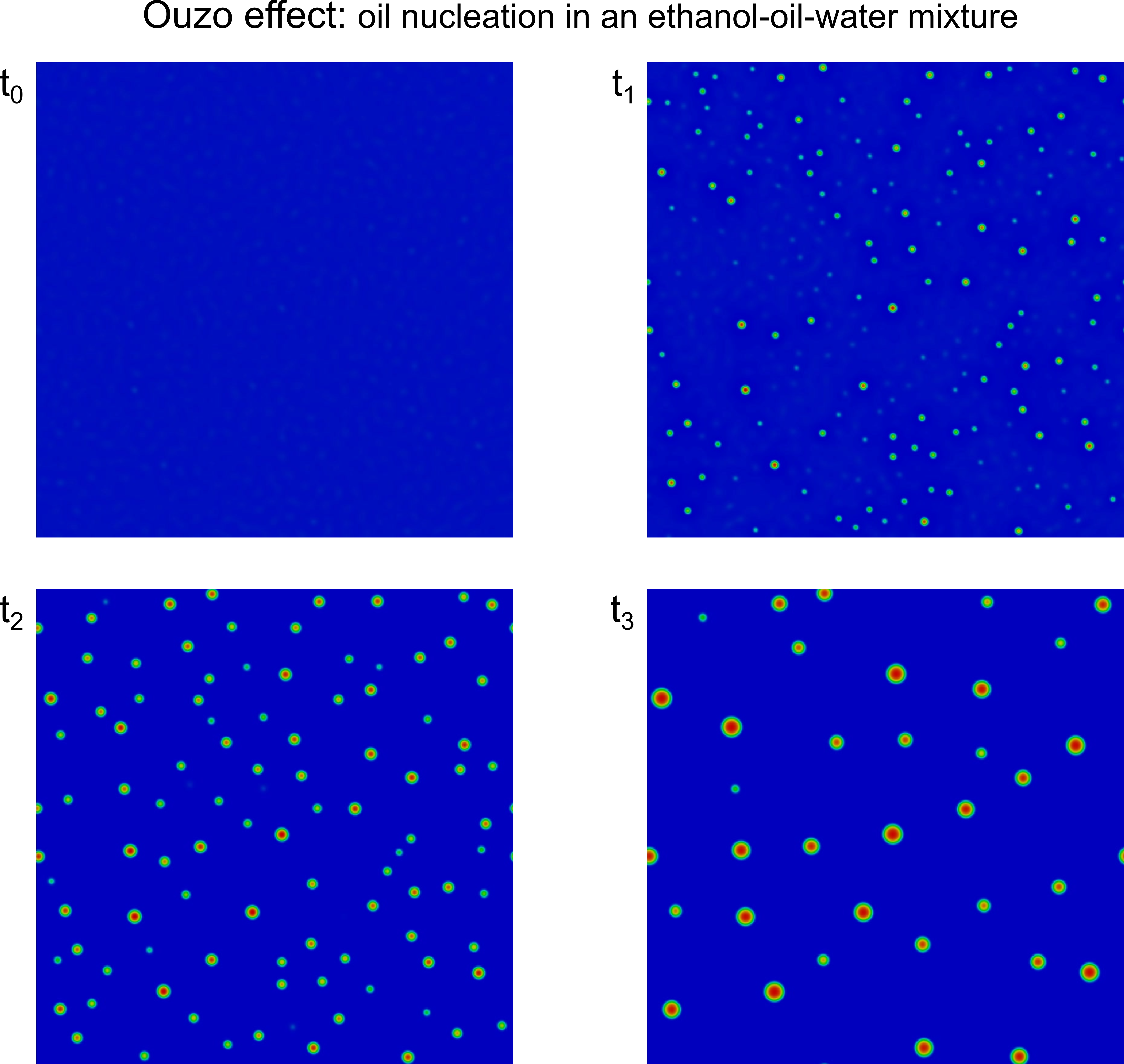
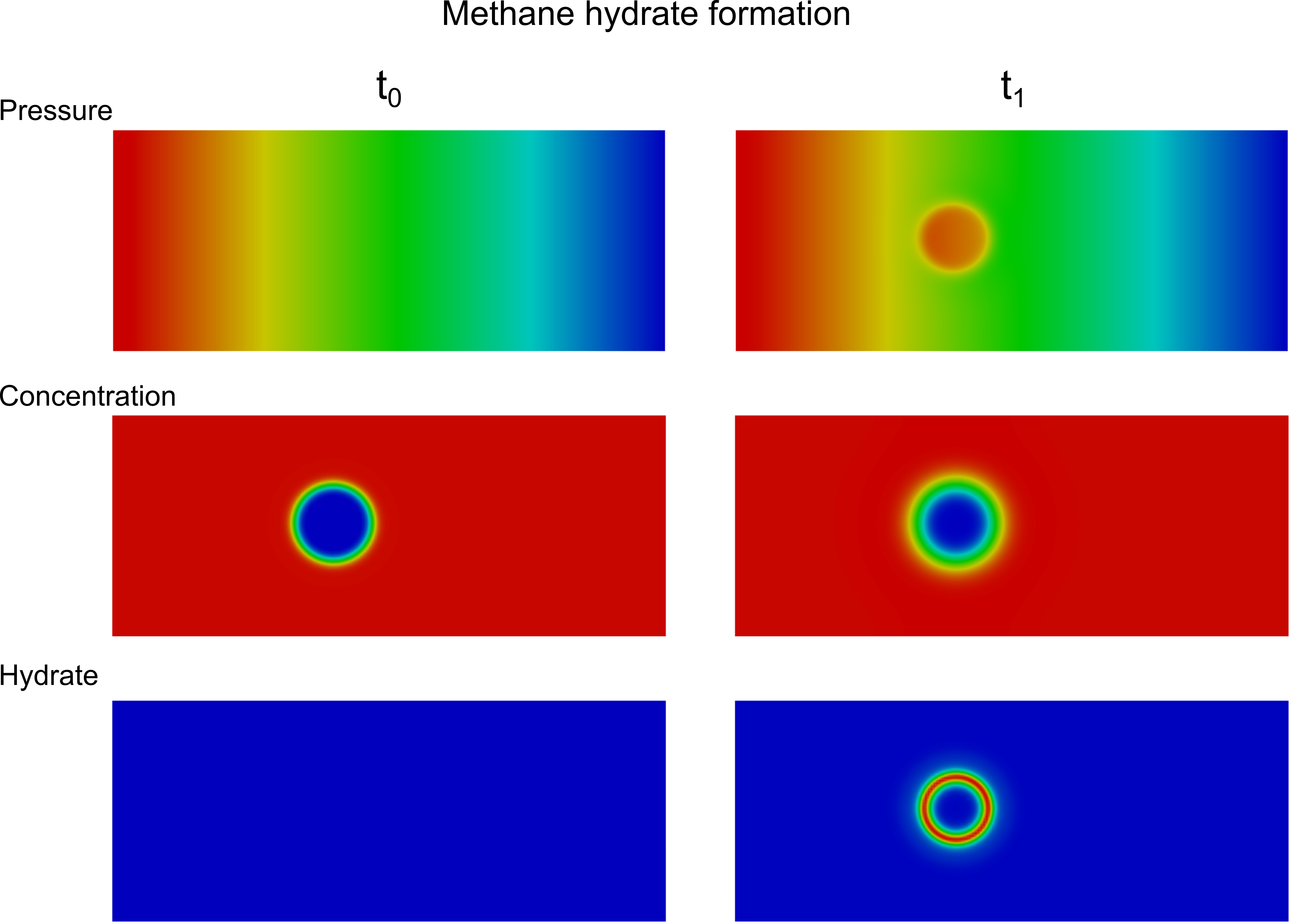
I have developed the phase-field formulation and the numerical implementation for solidification of binary mixtures, phase separation of ternary mixtures, and methane hydrate formation and dissociation. The Ouzo effect refers to the spontaneous nucleation of oil microdroplets in an ethanol-oil-water mixture, in which oil-water miscibility depends on the ethanol concentration. Methane hydrate formation and dissociation constitutes a two-component (methane and water) three-phase (solid, liquid, and gas) flow problem. The pictures show the nucleation of oil microdroplets in an ethanol-oil-water mixture (left) and the initial times of methane hydrate formation (right).
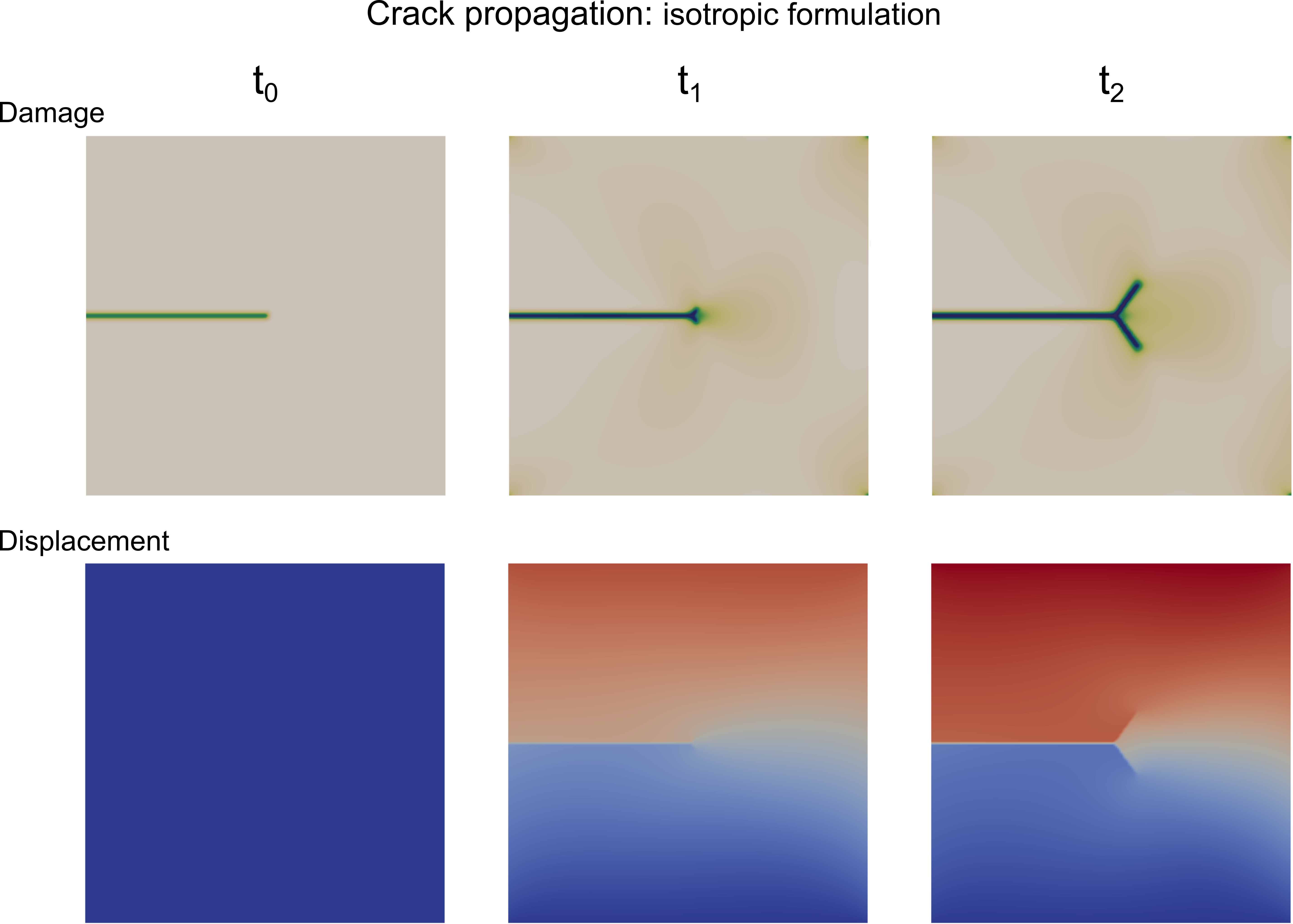
I have studied brittle fracture in elastic solids. The sharp crack discontinuity is modeled through the phase field. The momentum balance equation and the crack evolution equation are derived from a free energy functional. These equations can be coupled to a fluid mass conservation equation, which permits to model fluid-driven fracturing in solids. In the picture, single-edge notched shear test when crack propagation is allowed under tension and compression loading states (isotropic formulation).
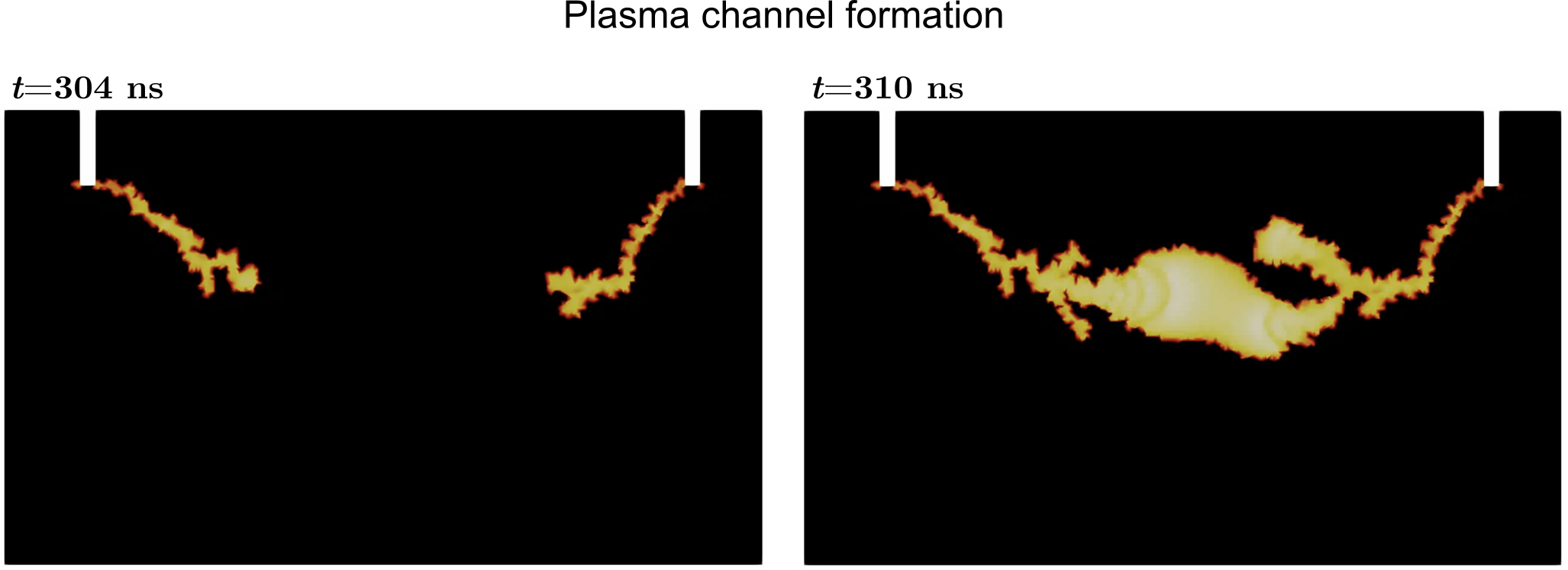
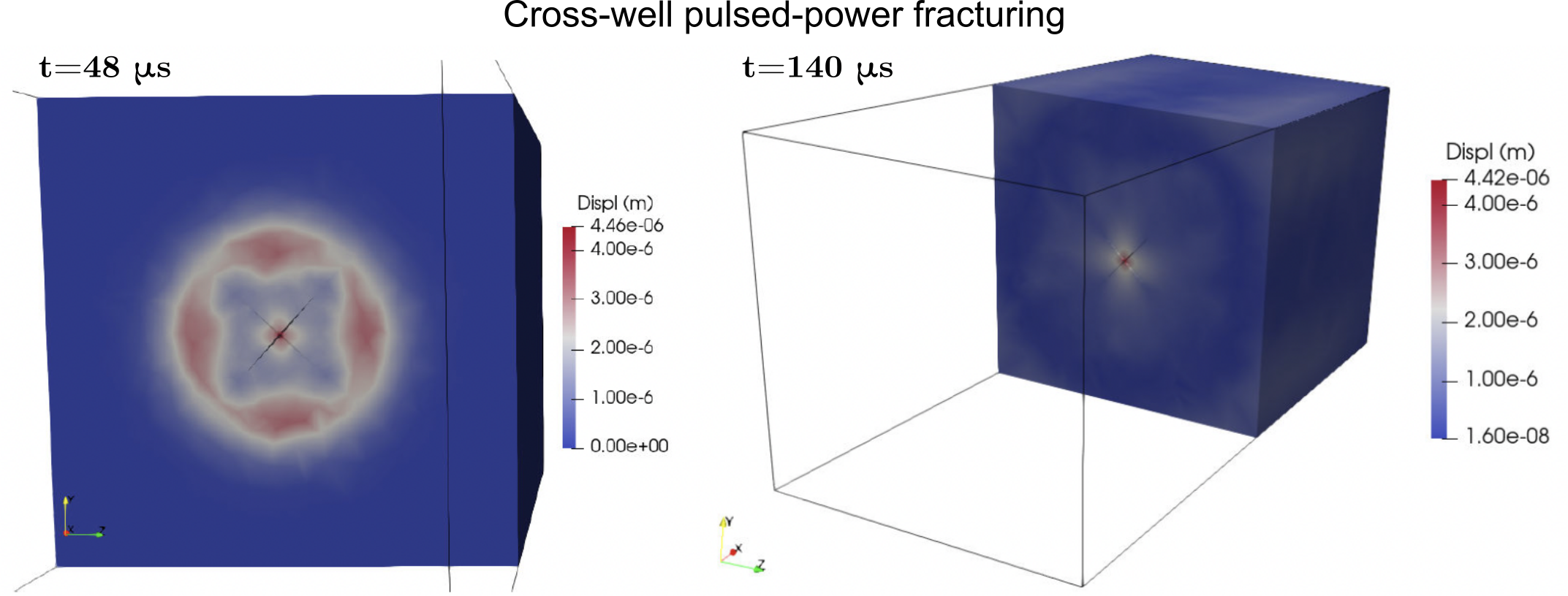
I have developed multiphysics simulators to reproduce the electro-stimulation of rocks via pulsed power and Joule heating. These models account for the formation of plasma upon release of high-voltage energy pulses, the electrical-to-mechanical energy conversion occurring during shockwave generation, and the dynamic fracturing of the rocks. The pictures show the rock dielectric breakdown modeled with the electric-charge continuity equation (left) and pulsed-power fracturing modeled using the split-node method (right).